PostgreSQL: Introduction
- also referred to as “Postgres”
- an object-relational database (ORDBMS)
- functions to store data securely
- functions to return data in response to requests from other software applications
- is ACID-compliant (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability)
- is transactional
- has native programming interfaces for C/C++, Java, .Net, Perl, Python, Ruby, Tcl, ODBC, among others
- manages concurrency by multiversion concurrency control (MVCC), which gives each transaction a “snapshot” of the database, allowing changes to be made without being visible to other transactions until the changes are committed
Reference: https://www.postgresql.org/about/
Installation
There is a number of ways to download & install Postgres. Since I’m working in MacOS, I installed Postgres with Homebrew.
# Update Homebrew
brew update
brew doctor
# Install Postgres
brew install postgresql
Reference: How to install PostgreSQL on a Mac with Homebrew and Lunchy (Moncef Belyamani, 2012)
Create a database
Now that Postgres is installed, we can create a database.
# init Postgres
initdb postgres
# start the postgres server
pg_ctl -D postgres start
# create your database
createdb mydb
initdb postgres -E utf8is used to create a new PostgreSQL database cluster- -E utf8 specifies the encoding to be utf8.
pg_ctl -D postgres -l logfile startis used to start the database server; it can also be used to initialize, start, stop (pg_ctl -D postgres stop), or control a PostgreSQL server- -D postgres specifies the file system location of the database configuration files
- -l logfile appends the server log output to specified filename
- start launches a new server
createdbis used to create a new PostgreSQL database
psql
psql is used to start a PostgreSQL interactive terminal. In the “help” (accessed by \h), we are given the following:
Make a table
Example taken from: How To Install and Use PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 16.04
To create a new table …
CREATE TABLE playground (
equip_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
type varchar (50) NOT NULL,
color varchar (25) NOT NULL,
location varchar(25) check (location in ('north', 'south', 'west', 'east', 'northeast', 'southeast', 'southwest', 'northwest')),
install_date date
);
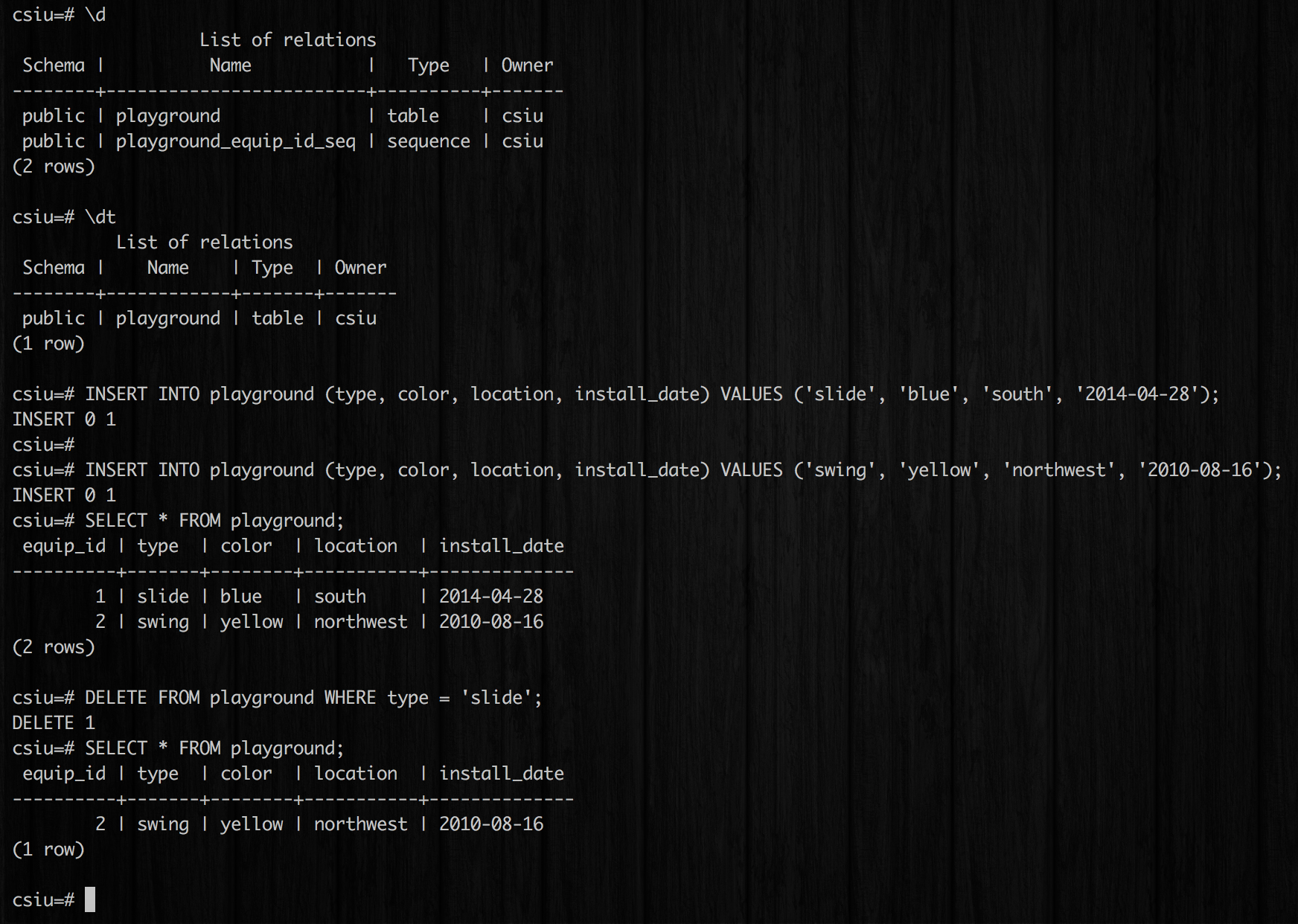
\dto see new table and\dtto see just the table without the sequence (a representation of the serial type given to the “equip_id” column).
To add records to the table …
INSERT INTO playground (type, color, location, install_date) VALUES ('slide', 'blue', 'south', '2014-04-28');
INSERT INTO playground (type, color, location, install_date) VALUES ('swing', 'yellow', 'northwest', '2010-08-16');
To query the table …
SELECT * FROM playground;
To delete records from the table …
DELETE FROM playground WHERE type = 'slide';
The output looks as follows:
Start/Stop Postgres as a background service at startup
You can also setup your Mac to start (or stop) Postgres as a background service at startup.
# brew tap homebrew/services
brew services start postgresql
brew services stop postgresql
brew services restart postgresql
Reference: How to Install PostgreSQL for Mac OS X (Albert Agram, 2014)